
Most of us have seen The Office–if you haven’t, you should watch it as soon as you finish reading this blog post–and some of us will remember a very specific episode of the show in which Toby plants radon test kits around the office, and Michael continually throws them out. Well, it turns out that Toby might just be saving Michael’s life (that is, if he isn’t the Scranton strangler). Radon is a dangerous chemical that can cause long term health problems, including lung cancer. This post will explore some of the health problems related to radon poisoning. We will also explain how radon testing works, and why it is important.
The first minute of the following video talks about what radon is and why it can be dangerous.
“These are silent killers”: Radon’s Effects on the Human Body
According to the EPA, radon gas is “a naturally-occurring radioactive gas that can cause lung cancer. Radon gas is inert, colorless and odorless.” Since radon lacks both odor and color, it is impossible for humans to know when it is present. Usually trace amounts of radon are present just about everywhere, including outside, but because of the air flow in outdoor environments, radon is not dangerous there.
Unfortunately, radon does become a health risk in indoor spaces, such as the office, or even your house. It’s a scary thought, isn’t it? Your house could be slowly poisoning you with radon gas, and you might not even know it.
Radon comes from the decomposition of the radioactive element uranium, which is used in nuclear power plants, so no wonder it’s not good for the lungs! It’s not quite as bad a carcinogen as smoking, but it still can have lasting and devastating effects. Radon levels are the highest underground, and sometimes the gas disperses into the air.
So what does radon do to your body, exactly? Well, when you breathe in, you aren’t just pulling oxygen into your lungs, you are also pulling in whatever other gases are present in the air around you, and often this includes radon. The radon gets into the lining of the lungs, and since it is a radioactive gas, it can cause mutations in the surrounding cells and tissues, sometimes eventually leading to cancer.
Around 21,000 people die from lung cancer as a result of radon poisoning each year. This is actually one of the most common reasons that non-smokers get lung cancer. Lung cancer due to prolonged exposure to dangerous levels of radon is highly preventable, so please watch for the signs.
Symptoms of radon gas poisoning include the following:
- Wheezing and coughing
- Coughing up blood
- Weight loss
Unfortunately, there is no way to purge your body of radon gas. It is important, if you have been exposed to high levels of radon, to make sure that you meet with a doctor and monitor yourself for cancer so you can catch it early if it begins.
In order to prevent any of this happening in the first place, the best thing to do is to put a radon gas detector in your home.

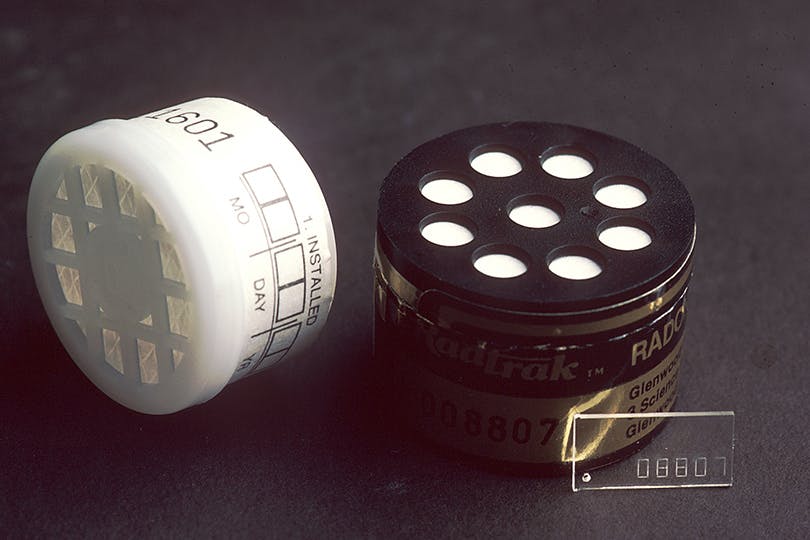
“This is a radon test kit, please don’t throw it out”: What is a Radon Test?
Okay, so if you’re now thoroughly terrified, let’s talk about the ways that you, like Toby, can prevent radon poisoning in your home and work environments. Toby was absolutely right to put a test kit in Michael’s office, and you should do the same.
So what is radon testing? There are three main testing methods for radon levels. Short-term radon test kits are similar to the ones Toby puts around the office. These usually cost 15-40 dollars, depending on the quality. They use activated charcoal or electret ion technology to measure radon levels in the building over the course of a few days (typically 2-7 days). These can be purchased at most hardware stores.
A long-term radon test will measure radon levels for a longer amount of time and is usually more accurate. These cost about 20-50 dollars. They usually take 90 days to a year, and measure alpha particles in the air over time. These can provide a more accurate annual average measurement of radon levels in the home than a short term radon meter.
Continuous radon detectors run on electricity and must be installed to monitor the atmosphere for elevated levels of radon gas within the home. A continuous radon detector is often more effective than a cheaper test kit, because they can notify you of the effects of radon continuously, instead of needing to be replaced. A radon monitor like this will cost a little more, usually in the 100-200 dollar range.
The other option for radon testing is to have a professional come in and test for radon. This usually costs about 110 dollars, and then the professional can also help with mitigation if they discover an issue. So costs for test kits and professional testing can range from 15-200 dollars, depending on your home and the accuracy you desire in your test.
When Radon Levels Become Dangerous
So when do high radon levels in the home become a problem? While you definitely shouldn’t be throwing away your radon test kits, you don’t have to worry until radon levels get too high. The average radon level in a home is 1.3 pCi/L. These are safe radon levels, but radon levels become dangerous when they hit 4 pCi/L. If your radon test results are at this level, you should have your home checked. In outdoor environments, the average radon level is 0.4 pCi/L. No matter where you are, radon will be present, it only becomes a problem when the radon concentration reaches dangerous levels.
Radon measurements, as you may have noticed, are in the units pCi/L, or picocuries per liter. This is a measurement of radiation from radon concentrations within a liter of air. The unit picocuries is named after Marie Curie, who discovered radiation in the early 1900s.
Unchecked radiation has been known to cause cancer and mutations since the 1960’s and 70’s, after nuclear bombs, power plants, and testing facilities began to notice problems in people who worked and lived around these areas. Since then, radon has also been discovered as one of the radioactive elements that can cause problems.
Radon Mitigation Methods
If radon levels inside a building begin to build up, there are ways to reduce radon levels. The department of health recommends using a radon mitigation system. Depending on the building’s foundation, mitigation methods will change. Below are listed a few of the most common radon mitigation systems.
- Sub-slab suction – This mitigation method pulls radon directly from beneath the home’s foundation and vents it outside.
- Drain tile suction – A pipe is run into the drain tile in the basement and around a house and vents the soil gases outside.
- Sub-membrane – These are used in crawl spaces, and they use a plastic sheet to cover the dirt on the floor. This sheet then goes up the wall. A piece of radon pipe is put through the plastic sheet to vent the gas from the crawl space outside.
Most radon mitigation systems will cost from 1,500 to 2,500 dollars, which is expensive enough that buildings often will not have them installed automatically. So it is important to test for radon yourself to make sure that a mitigation system is even necessary for your specific situation. If you find that you do need radon reduction, you should contact the state radon office to find a licensed professional to come and assess your home.
This professional will let you know what kind of mitigation system will work best for your home, and if they are a contractor, they will be able to help you install a mitigation system. If they are not a contractor, you have a couple of options. You can hire another contractor to come and install the system, or you can install a radon system yourself! If you do this, make sure that you are doing so correctly. It may be worth it to have the professional come back to make sure that you have installed the system correctly.

Other Important Environmental Levels to Check
Radon is not the only gas that can be harmful if levels get too high. You should also make sure to monitor your carbon monoxide levels. Like radon, carbon monoxide is colorless and odorless. It is produced as a byproduct when fossils such as gasoline, natural gas, or coal are burned. These fossil fuels contain high levels of carbon, and when they are burned in a process called incomplete combustion, the carbon reacts with oxygen in the air to form carbon monoxide gas. Many homes have heating and cooling elements, such as a furnace or a water heater, that are powered by fossil fuels, and thus, carbon monoxide gas can be emitted in these homes. Usually, the levels of CO emission remain low enough not to be dangerous with proper ventilation.
If you come into contact with too much carbon monoxide gas (otherwise referred to as carbon monoxide poisoning), the symptoms can include the following:
- Nausea or stomach pain
- Blurry vision
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Fainting
Eventually, high levels of exposure to CO can lead to brain damage. So it’s important to keep yourself protected with a CO detector. These are available from a variety of locations and are sold by Cove as well.
While CO is not a radioactive gas, it is still dangerous, and it is important to make sure your home is safe from its effects. Installing a CO detector is definitely worth the minimal costs.
Other important tests and checks for your home’s environment include flood and freezing, and fire detectors. These are important to keep your home safe from the dangers that can occur as a result of environmental change. Luckily, fire, fooding, and freezing are a little easier for us to detect with our senses, but it’s still important to have these detectors up to protect you and your family.
At Cove, we truly care about you and your family. While we do not offer radon testing services, we do offer other environmental detectors and burglary/trespassing alarms that are easy-to-use and linked to one accessible touch control panel. We offer DIY systems that you can personalize and easily install to get you the best security around. We want you to be able to go to sleep at night knowing that you and your family are protected.
